[C58] An Efficient Ventricular Arrhythmias Detection on Microcontrollers with Optimized 1D CNN
Abstract
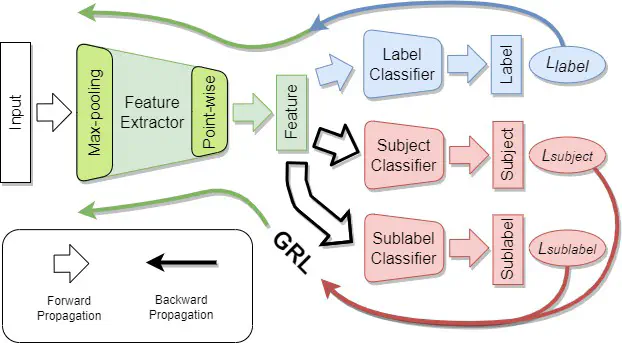
Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) is a major public health concern. One of the critical risk factors for SCD is life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias (VAs) such as ventricular fibrillation (VF) and ventricular tachycardia (VT). The use of implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) which is designed to detect and respond to VAs, plays a crucial role in significantly improving survival chances. However, the inherent constraints of ICD, operating in a power-constrained and memory-limited environment, intensify the challenges of implementing a real-time VA detection system on a resource-constrained microcontroller platform. This paper proposes a solution that leverages a 1D convolutional neural network (CNN) with key optimizations, including adaptive max-pooling, point-wise convolution, and a multi-objective gradient reversal layer (GRL). The model demonstrates high accuracy in distinguishing VAs and Non-VAs from single-channel intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals obtained from an ICD. The experiments and analysis conducted demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model. The proposed model achieves a Fβ score of 0.99265, a generalization score of 0.9375, a memory occupation of 24.332 KiB, and an inference latency of 2.593 ms, outperforming the top performing models from the 2022 TinyML Design Contest in terms of detection accuracy and generalizability while maintaining competitive inference latency and memory occupation.